by Thomas Lethenborg | Aug 21, 2020 | News
Quality Policy and Standards
As a technology leader in mobile health (mHealth) solutions for mental health, Monsenso is ISO 13485 certified.
ISO 13485 is the gold standard for medical device companies to ensure the quality, safety and efficacy of products in the medical device field. This certification ensures that the product in question, consistently meets customer requirements and regulatory requirements applicable to medical devices and other related services.
“Monsenso adheres to the highest security standards. Beyond, being ISO 13485, Monsenso holds the ISO 27001 certifications, a TGA certification and class 1 CE mark.” says Thomas Lethenborg, CEO at Monsenso.
You can download this article as PDF in English.
For additional information contact:
Bettina van Wylich
Chief Marketing Officer
Monsenso
+45 22704724
wylich-muxoll@monsenso.com

by Thomas Lethenborg | Aug 21, 2020 | News, Press releases
Quality Policy and Standards
As a technology leader in mobile health (mHealth) solutions for mental health, Monsenso is ISO 13485 certified. ISO 13485 is the gold standard for medical device companies to ensure the quality, safety and efficacy of products in the medical device field. This certification ensures that the product in question, consistently meets customer requirements and regulatory requirements applicable to medical devices and other related services.
“Monsenso adheres to the highest security standards. Beyond, being ISO 13485 certified, Monsenso holds the ISO 27001 certification and class 1 CE mark.” says Thomas Lethenborg, CEO at Monsenso.

For additional information contact:
Jennifer Highland
Marketing and Communications Manager
Monsenso
+45 81 71 7713
highland@monsenso.com

by Thomas Lethenborg | Jun 21, 2016 | Blog, Mental Illness, mHealth
According to a recent statement by the new American Heart Association (AHA), major depressive disorder and bipolar disorder should be recognized as moderate risk factors for atherosclerosis and early cardiovascular disease. [1]
In 2011, the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute identified four conditions (chronic inflammatory disease, human immunodeficiency virus, Kawasaki disease, and nephritic syndrome) that lead youths to a mild risk of developing cardiovascular disease before they reach 30. [2]
The statement released a few days ago, reveals that depression and bipolar disorder meet the same criteria as these conditions. Moreover, these two behavioural disorders are more widespread than the previous mentioned conditions combined.
These studies showed evidence of a link between paediatric depression and bipolar disorder with premature cardiovascular mortality. Cardiovascular risk factors for these teens include obesity, insulin resistance and diabetes, dyslipidemia, and hypertension.[1] According to the statement, depression and bipolar disorder are the first- and fourth-most disabling conditions, among adolescents worldwide.
After the report had been unveiled, researchers from schools around the U.S. and Canada looked at existing studies on mood disorders in people under the age of 30. Researchers looked specifically into youths suffering from depression or bipolar disorder with cardiovascular markers such as high pressure and cholesterol. They found a significant connection between having depression or bipolar disorder and increased odds of high blood pressure, high cholesterol, obesity (especially belly fat), type 2 diabetes, and hardening of the arteries. [3]
This discovery denotes that healthcare providers should track physical activity levels and food intake as well as metabolic monitoring is crucial for these young patients as a preventive measure.
However, to monitor cardiovascular markers, physical activity and food intake, of thousands of young patients who also suffer from mental illness is not an easy task. Although, there are hundreds of smartphone applications tracking physical activity and counting calories, these apps are personal, and clinicians do not have access to an individual’s data. Nevertheless, with the Monsenso mobile health (mHealth) solution, this cumbersome task becomes easy and achievable.
The Monsenso mHealth solution enables clinicians to access a patient’s data on a daily basis. Every day, youths would be reminded to fill in a self-assessment with important information that could include the number of hours they slept, the amount of unhealthy food they have eaten, and if they realized any physical activity throughout their day. Additionally, the smartphone can also collect physical activity and mobility data, based on the smartphone’s inbuilt accelerometer and GPS locator.
The Monsenso mHealth solution, especially designed to monitor behavioural data of patients suffering from mental illness, can in this way help clinicians monitor any unhealthy habits of patients with risk of developing cardiovascular disease.
Further, with the customisable action plans, each youth could follow “contingency plans” if they experience some symptoms related to their mental illness or if they have engaged in unhealthy activities. For example, a special trigger could set up if a youth has indulged in unhealthy food for several days in a row, or has had a low level of physical activity. The action plan listed for this trigger could then encourage individuals to engage in physical activities and and to try to avoid sugar and fat during the upcoming week.
References:
[1] Browser,D Medscape. Depression, Bipolar Disorder in Teens are CVD Risk Factors: AHA (2015, August 10) http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/849312
[2] American Heart Association. Young people with mood disorders have increased risk of developing early cardiovascular disease (2015, August 11)
http://blog.heart.org/young-people-with-mood-disorders-have-increased-risk-of-developing-early-cardiovascular-disease/
[3] Walton, A Forbes. Teens with depression, bipolar disorder, should be screened for heart disease, experts say. (2015, August 11) http://www.forbes.com/sites/alicegwalton/2015/08/11/depressed-teens-may-be-at-higher-risk-for-heart-disease/
Goldstein BI, Carnethon MR, Matthews KA, et al. Major depressive disorder and bipolar disorder predispose youth to accelerated atherosclerosis and early cardiovascular disease. Circulation 2015.

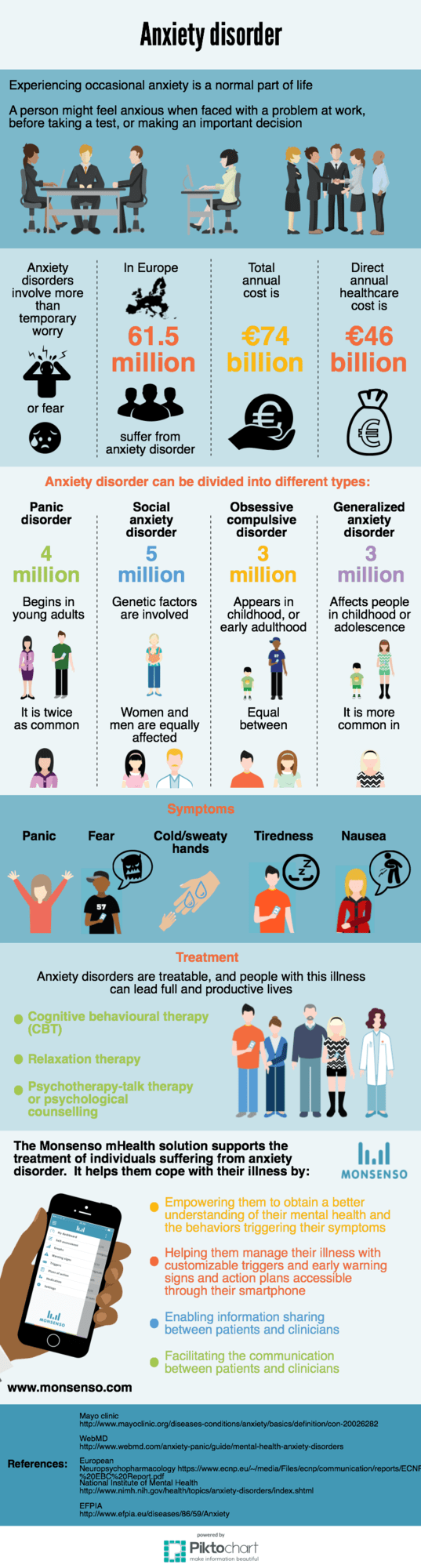
by Thomas Lethenborg | Nov 3, 2015 | Anxiety
Experiencing occasional anxiety is a normal part of life. However, people with anxiety disorders frequently have intense, excessive and persistent worry and fear about everyday situations. Often, anxiety disorders involve repeated episodes of sudden feelings of intense anxiety and fear or terror that reach a peak within minutes (panic attacks) [1].
Anxiety is the primary symptom of several conditions, including:
- Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD)
- Panic attacks
- Phobias
- Post-traumatic stress disorder
- Social anxiety disorder [2]
- Symptoms of GAD
- Restlessness
- Sense of dread
- Feeling constantly “on edge”
- Difficulty concentrating
- Irritability
- Dizziness
- Tiredness
- Fast or irregular heartbeat
- Muscle aches and tension
- Trembling or shaking
- Shortness of breath
- Headache
- Insomnia [2]
The two main treatments for anxiety disorders are psychotherapy and medication. It is often beneficial to combine both. It may take some trial and error to discover which treatments work best for an individual.
Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy, also known as talk therapy or psychological counselling, involves working with a therapist to reduce a person’s anxiety symptoms. Sometimes, it can be an effective treatment on its own [3].
Cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) is one of the most effective forms of psychotherapy for anxiety disorders. A short-term treatment, cognitive behavioural therapy focuses on teaching individuals specific skills to return gradually to the situations they avoided due to their anxiety [3].
Applied relaxation focuses on relaxing your muscles in a particular way during situations that usually cause anxiety. The technique needs to be taught by a trained therapist, but involves:
- Learning to relax one’s muscles
- Learning to relax one’s muscles quickly and in response to a trigger, such as the word “relax”
- Relaxing one’s muscles in situations that make a person anxious [2]
Medication
- Antidepressants – this type of medications influences the activity of brain chemicals (neurotransmitters) thought to play a role in anxiety disorders
- Buspirone – an anti-anxiety medication called buspirone may be used on an ongoing basis. As with most antidepressants, it typically takes up to several weeks to become fully effective
- Benzodiazepines – this type of medication are used only for relieving acute anxiety on a short-term basis. Because they can be habit-forming, these medications aren’t a good choice if you’ve had problems with alcohol or drug abuse [1]
The Monsenso mHealth solution for behavioural disorders is currently being used to support the treatment of individuals suffering from bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, depression, and borderline personality disorder.
Although there isn’t any ongoing research on anxiety, it can definitely be used to support the treatment of anxiety with in conjunction with CBT.
Individuals can obtain an overview of their historic levels of anxiety and try to identify the behavioural patterns that trigger their symptoms. Based on their historical records they can learn to predict situations of risk and take preventive measures to avoid or minimize any adverse reactions. Additionally, the Monsenso smartphone app also provides individuals with customized action plans and a secure communication channel with their clinic when they need it the most.
References:
[1] Anxiety. Mayo Clinic.
http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/anxiety/basics/definition/con-20026282
[2] Anxiety. National Institute of Mental Health.
http://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/anxiety-disorders/index.shtml
[3] Anxiety. National Health Service (NHS) UK
http://www.nhs.uk/conditions/anxiety/Pages/Introduction.aspx