Connected health or technology-enabled care (TEC) is the collective term used for telecare, telehealth, telemedicine, mHealth, digital health, and eHealth services. TEC is now seen as a fundamental part of the solution to solve many healthcare challenges.
TEC helps people self-manage their health and wellbeing, alert healthcare professionals in case of any changes in an individual’s condition and support medication adherence.
It also helps clinicians and care providers deliver more efficient and cost-effective care.
Digital technology is advancing exponentially, and its cost is becoming more affordable. The need for more cost-effective healthcare is rising. Now more than ever, healthcare authorities need to adopt new technologies to help meet this demand.
Key trends
An aging population
The population is increasing, and people are living longer. These two factors, in addition to a rise in chronic conditions, present new healthcare challenges.
In the United States, population projection reports that older adults currently make up about 15% of the population, and by the year 2060 is estimated to amount to 23.5%.
There are similar numbers reported for Europe, where the group of 65-year old or older make up 19% of the population and is predicted to amount to 29% of the total population by the year 2080.
Use of mobile devices is increasing amongst all age groups
A 2019 report conducted by Provision Living, a senior living community in the U.S., revealed that on average, Baby Boomers (born between 1946 and 1964) and millennials (born between 1981 and 1995) spend on average, five hours a day on their smartphones.
Smartphone adoption among Americans:
- Aged 50 to 59 is 86%
- Aged 60 to 69 is 81%
- Aged 70+ is 62%
Other market drivers
The demand for apps and wearable devices is also being driven by an increased focus on personalised care. Large pharmaceutical companies are now using apps and wearables to gather valuable health-related patient data, support their research, and provide an holistic service to patients.
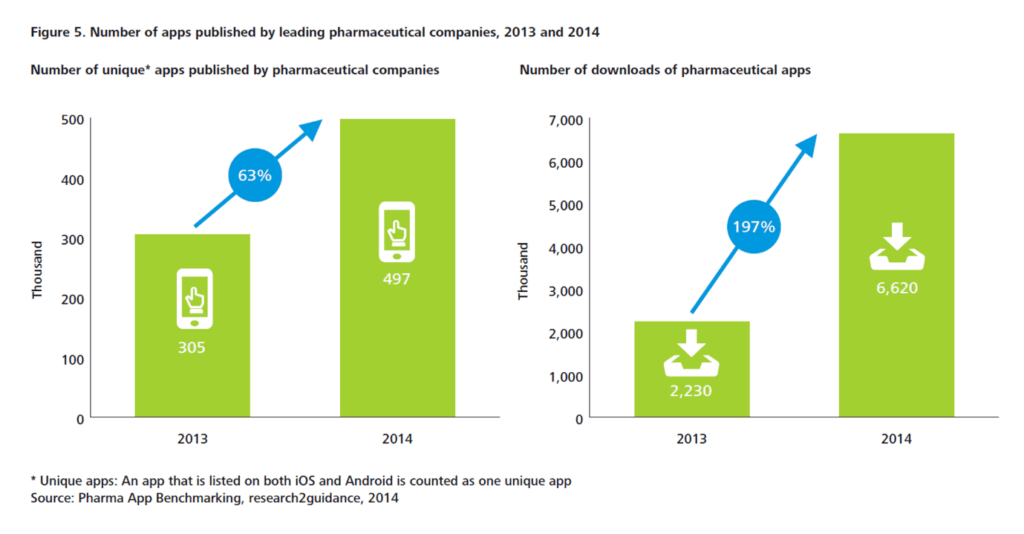
In 2014, the leading pharmaceutical companies had an increase of 63 % in unique apps compared to 2013. In just one year, the total number of downloads of pharmaceutical apps increased by 197% as shown in Figure 1. These apps deliver education and training, can titrate medication and monitor compliance.
Figure 1. The number of apps published by leading pharmaceutical companies, 2013 and 2014.
There has also been an increase in online patient communities, using social media as a platform to exchange experiences with patients and carers.
Increasing patient trust in health apps
There is strong evidence that patients are now more than ever concerned about self-care, and they are interested in boosting their health and wellbeing. In addition to this, health technology companies are working to improve the quality of apps, increase user confidence and trust, and launch informed decision-making in app selection for health professionals, patients and the public.
Agencies like the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), or NHS Choices and its NHS Health Apps Library have developed criteria that judge apps for safety and technical proficiency. For example, for apps to be included on the NHS Choices search website, which in early 2015 lists around 150 apps, they must be reviewed by a technical team (testing relevance, legal compliance and data protection), then by a clinical team (to test scientific rigour).
PatientView is an independent organisation that has developed a systematic method of appraising health apps. Until April 2015, there were 363 apps recommended for the Apple platform and 236 for Android, with smaller numbers recommended for use on other platforms.
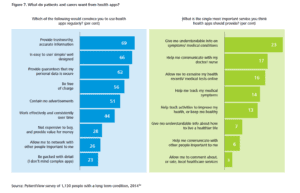
In 2014, PatientView undertook a survey of 1,130 patient group members to identify what people want from health apps as shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2. What do patients and carers want from health apps?
References:
Connected Health: How Digital technology is transforming health and social care. Deloitte Health.
Forget Generational Stereotypes, Baby Boomers Are Just As Addicted To Smart Phones As Millennials.
Older Adults Keep Pace on Tech Usage.
An Aging Population, Larger Chronic Disease Burden, and Reliance on Digital Self-Management Tools Require Contributions from Nurse Informaticians.









